Hemorrhagic
Hemorrhage is the medical term for bleeding. It most often refers to excessive bleeding. Hemorrhagic diseases are caused by bleeding, or they result in bleeding (hemorrhaging).
Related topics include:
- Primary thrombocythemia (hemorrhagic thrombocythemia)
Primary thrombocythemia
Essential thrombocythemia (ET) is a condition in which the bone marrow produces too many platelets. Platelets are particles in the blood that aid in...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Yellow fever
Yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral infection spread by mosquitoes.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding disorders
Bleeding disorders
Bleeding disorders are a group of conditions in which there is a problem with the body's blood clotting process. These disorders can lead to heavy a...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Ebola fever
Ebola fever
Ebola is a severe and often deadly disease caused by a virus. Symptoms include fever, diarrhea, vomiting, bleeding, and often, death. Ebola can occu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dengue hemorrhagic fever
Dengue hemorrhagic fever
Dengue fever is a virus-caused disease that is spread by mosquitoes. Dengue in its mild form causes fever and a rash and lasts about a week. Severe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vitamin K deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin. Your body stores vitamin K in the liver and other body tissues, including the brain, heart, pancreas, and bone....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Halstead SB. Dengue fever, dengue hemorrhagic fever, and severe dengue. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 315.
Schafer AI. Approach to the patient with bleeding or thrombosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 157.
Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company; 2021. www.tabers.com/tabersonline/view/Tabers-Dictionary/765242/all/hemorrhage?q=Hemorrhagic&ti=0. Accessed April 1, 2025.
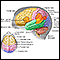
Intracerebral hemorrhage - illustration
Intracerebral hemorrhage may be caused by trauma (brain injury) or abnormalities of the blood vessels (aneurysm or angioma), but it is most commonly associated with high blood pressure (hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage).
Intracerebral hemorrhage
illustration
Intracerebral hemorrhage - illustration
Intracerebral hemorrhage may be caused by trauma (brain injury) or abnormalities of the blood vessels (aneurysm or angioma), but it is most commonly associated with high blood pressure (hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage).
Intracerebral hemorrhage
illustration
Review Date: 4/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.