Stimulants
Stimulants are chemicals (usually drugs or medicines that increase your heart rate, breathing rate, and brain function. Some stimulants affect only a specific organ, such as the heart, lungs, brain, or nervous system.
Epinephrine is a stimulant. It is given during cardiac arrest to stimulate the heart and help restore the heartbeat.
Cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating. When this happens, blood flow to the brain and the rest of the body also stops. Cardia...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOther times, stimulants can cause unwanted side effects. For example, pseudoephedrine found in some cold medicines can increase the heart rate. Caffeine, found in many beverages, may also increase the heart rate or cause a tremor.
References
Taber's Cyclopedic Medical Dictionary. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company; 2021. www.tabers.com/tabersonline/view/Tabers-Dictionary/762879/all/stimulant. Accessed December 17, 2024.
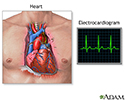
Electrocardiogram (ECG) - illustration
An electrocardiogram is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. This includes the rate and regularity of beats as well as the size and position of the chambers, any damage to the heart, and effects of drugs or devices to regulate the heart.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
illustration
Electrocardiogram (ECG) - illustration
An electrocardiogram is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. This includes the rate and regularity of beats as well as the size and position of the chambers, any damage to the heart, and effects of drugs or devices to regulate the heart.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.