Retina
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eyeball. Images that come through the eye's lens are focused on the retina. The retina then converts these images to electric signals and sends them along the optic nerve to the brain.
The retina most often looks red or orange because there are many blood vessels right behind it. An ophthalmoscope allows your health care provider to see through your pupil and lens to the retina. Sometimes photos or special scans of the retina can show things that the provider cannot see just by looking at the retina through the ophthalmoscope. If other eye problems block the provider's view of the retina, ultrasound can be used.
Ophthalmoscope
Ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the back part of the eye (fundus), which includes the retina, optic disc, choroid, and blood vessels.
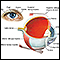
Ultrasound
An eye and orbit ultrasound is a test to look at the eye area. It also measures the size and structures of the eye.
Anyone who experiences these vision problems should get a retinal examination:
- Changes in sharpness of vision
- Loss of color perception
- Flashes of light or floaters
- Distorted vision (straight lines look wavy)
References
Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Diseases of the visual system. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 391.
Reh TA, Eldred KC, Sridhar A. The development of the retina. In: Sadda SVR, Sarraf D, Freund KB, et al, eds. Ryan's Retina. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 15.
Schubert HD. Structure of the neural retina and retinal pigment epithelium. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 6.1.
Eye - illustration
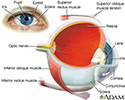
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
Review Date: 4/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.