Primary amyloidosis
Amyloidosis - primary; Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis; Primary systemic amyloidosis; Primary localized amyloidosisPrimary amyloidosis is a rare disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid deposits.
Causes
The cause of primary amyloidosis is not well understood. Genes may play a role.
The condition is related to abnormal and excess production of specific proteins. The proteins build up in certain organs. This makes it harder for the organs to work correctly.
Primary amyloidosis can lead to conditions that include:
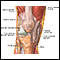
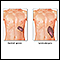
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (due to protein deposits in the nerve)
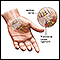
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in which there is excessive pressure on the median nerve at the wrist. This is the nerve that allows feeling a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart muscle damage (cardiomyopathy) leading to congestive heart failure
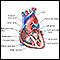
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is disease in which the heart muscle becomes weakened, stretched, or has another structural problem. It often contributes to the hear...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCongestive heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intestinal malabsorption
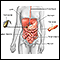
Malabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in (absorb) nutrients from food.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver swelling and malfunction
- Kidney failure
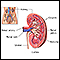
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nephrotic syndrome (a group of signs that includes protein in the urine, low protein levels in the blood, high cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, and swelling throughout the body)
Nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a group of symptoms and abnormal test results that include protein in the urine, low blood protein levels in the blood, high ch...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve problems (neuropathy)
- Orthostatic hypotension (drop in blood pressure when you stand up)
Orthostatic hypotension
Low blood pressure occurs when blood pressure is below normal. This means the heart, brain, and other parts of the body may not get enough blood. I...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the organs affected. This disease can affect many organs and tissues, including the tongue, intestines, skeletal and smooth muscles, nerves, skin, ligaments, heart, liver, spleen, kidneys, and bladder.
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Fatigue
- Numbness of hands or feet
- Shortness of breath
- Skin changes
- Swallowing problems
- Swelling in the arms and legs
- Swollen tongue
- Weak hand grip
- Weight loss or weight gain
Other symptoms that may occur with this disease:
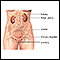
- Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output means that you produce less urine than normal. Most adults make at least 500 milliliters of urine in 24 hours (a little over ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diarrhea
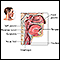
- Hoarseness or changing voice
Hoarseness or changing voice
Hoarseness refers to difficulty making sounds when trying to speak. Vocal sounds may be weak, breathy, scratchy, or husky, and the pitch or quality ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain
- Weakness
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you. You will be asked about your medical history and symptoms. A physical exam may show that you have a swollen liver or spleen, or signs of heart or nerve damage.
Swollen liver
Enlarged liver refers to swelling of the liver beyond its normal size. Hepatomegaly is another word to describe this problem. If both the liver and ...

Spleen
Splenomegaly is a larger-than-normal spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the belly.
The first step in diagnosing amyloidosis should be blood and urine tests to look for abnormal proteins.
Other tests depend on your symptoms and the organ that may be affected. Some tests include:
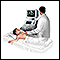
- Abdominal ultrasound to check the liver and spleen
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart tests, such as an ECG, echocardiogram, or MRI
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleEchocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
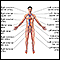 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
Heart magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use ra...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney function tests to check for signs of kidney damage (nephrotic syndrome or renal insufficiency)
Tests that can help confirm the diagnosis include:
- Abdominal fat pad aspiration
- Bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart muscle biopsy
Heart muscle biopsy
Myocardial biopsy is the removal of a small piece of heart muscle for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rectal mucosa biopsy
Rectal mucosa biopsy
A rectal biopsy is a procedure to remove a small piece of tissue from the rectum for examination.
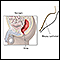 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment may include:
- Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
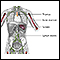 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stem cell transplant
Stem cell transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Organ transplant
If the condition is caused by another disease (secondary amyloidosis), that disease should be aggressively treated. This may improve symptoms or slow the disease from getting worse. Complications such as heart failure, kidney failure, and other problems can sometimes be treated, when needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do depends on which organs are affected. Heart and kidney involvement may lead to organ failure and death. Body-wide (systemic) amyloidosis can lead to death within 2 years.
Systemic
Systemic means affecting the entire body, rather than a single organ or body part. For example, systemic disorders, such as high blood pressure, or s...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleWhen to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of this disease. Also call if you have been diagnosed with this disease and have:
- Decreased urination
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the ankles or other body parts that does not go away
Prevention
There is no known prevention for primary amyloidosis.
References
Buxbaum JN. The systemic amyloidoses. In: Hochberg MC, Gravallese EM, Smolen JS, van der Hejide D, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH, eds. Rheumatology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 177.
Gertz MA, Dispenzieri A. Amyloidosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 174.
Gertz MA, Buadi FK, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR. Immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis (primary amyloidosis). In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 93.
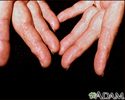
Amyloidosis of the fingers - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to the extracellular deposition of a protein called amyloid. This protein deposition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging, or may occur with several other conditions. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can affect the skin as nodular deposits on the fingers.
Amyloidosis of the fingers
illustration
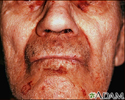
Amyloidosis of the face - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to deposits of a protein (called amyloid) in the tissues. This condition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can cause a patchy, bruised appearance to the skin. Bruises of the skin around the eyes are referred to as the characteristic pinched purpura.
Amyloidosis of the face
illustration
Amyloidosis of the fingers - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to the extracellular deposition of a protein called amyloid. This protein deposition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging, or may occur with several other conditions. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can affect the skin as nodular deposits on the fingers.
Amyloidosis of the fingers
illustration
Amyloidosis of the face - illustration
Amyloidosis refers to deposits of a protein (called amyloid) in the tissues. This condition can affect multiple organs. The deposition of amyloid may be a by-product of normal aging. In this picture, we see how amyloidosis can cause a patchy, bruised appearance to the skin. Bruises of the skin around the eyes are referred to as the characteristic pinched purpura.
Amyloidosis of the face
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.